Hey there, tech explorer! 👋
I’m Vikas Sankhla, your friendly Full Stack Developer and the founder of Web Codder. Today, we’re going to learn about CI/CD, which stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment. Think of it as your application’s superpower to deliver updates faster and more reliably! 💪
🌟 What is CI/CD?
Imagine you’re building a LEGO castle. Every time you add a new piece, you want to make sure it fits perfectly and doesn’t break the structure. CI/CD does the same for your code. It automatically tests and deploys your application whenever you make changes, ensuring everything works smoothly. 🏰🧱
🧱 Key Concepts
Let’s break down some important terms:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Continuous Integration (CI) | Automatically testing and integrating code changes |
| Continuous Deployment (CD) | Automatically deploying code changes to production |
| Pipeline | A series of automated steps for building, testing, and deploying code |
| GitHub Actions | A tool to automate workflows directly from your GitHub repository |
| Docker | A platform to package applications into containers |
| ECR (Elastic Container Registry) | AWS service to store Docker images |
| ECS (Elastic Container Service) | AWS service to run Docker containers |
🛠️ Setting Up CI/CD with GitHub Actions
Step 1: Create a GitHub Repository
- Go to GitHub and create a new repository.
- Clone the repository to your local machine.
- Add your application code to the repository.
Step 2: Add a GitHub Actions Workflow
- In your repository, create a
.github/workflowsdirectory. - Inside this directory, create a file named
ci-cd.yml. - Add the following content to the file:
yamlCopyEditname: CI/CD Pipeline
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
build-and-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Docker
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
- name: Log in to Amazon ECR
uses: aws-actions/amazon-ecr-login@v1
- name: Build, tag, and push image to Amazon ECR
env:
ECR_REGISTRY: ${{ secrets.ECR_REGISTRY }}
ECR_REPOSITORY: ${{ secrets.ECR_REPOSITORY }}
IMAGE_TAG: ${{ github.sha }}
run: |
docker build -t $ECR_REGISTRY/$ECR_REPOSITORY:$IMAGE_TAG .
docker push $ECR_REGISTRY/$ECR_REPOSITORY:$IMAGE_TAG
- name: Deploy to Amazon ECS
uses: aws-actions/amazon-ecs-deploy-task-definition@v1
with:
task-definition: ecs-task-def.json
service: my-service
cluster: my-cluster
wait-for-service-stability: true
This workflow will build your Docker image, push it to Amazon ECR, and deploy it to Amazon ECS whenever you push changes to the main branch.
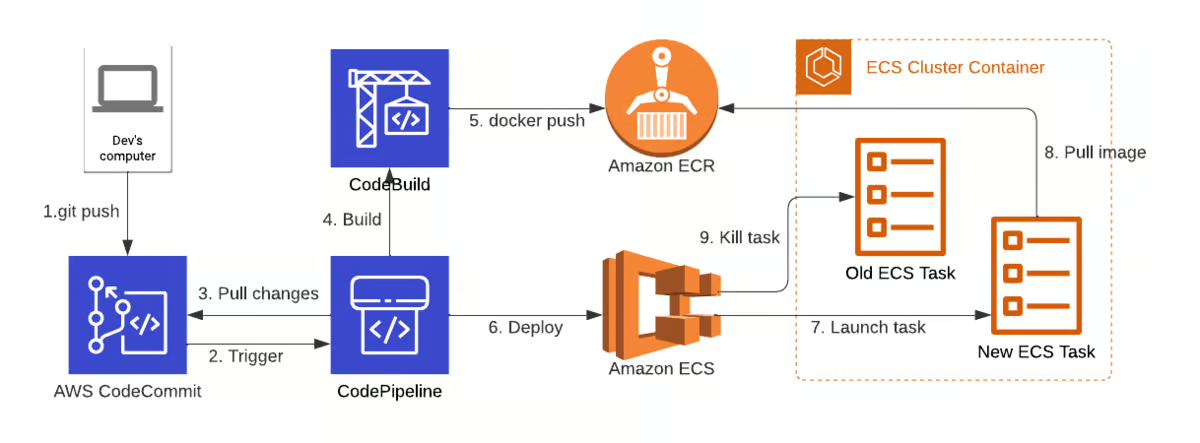
🐳 Automating Docker Builds and Deployment to ECS/ECR
Docker allows you to package your application with all its dependencies into a container. Here’s how you can automate building and deploying Docker containers:
- Build the Docker Image: Use the
docker buildcommand to create an image of your application. - Push to Amazon ECR: Use the
docker pushcommand to upload your image to Amazon ECR. - Deploy to Amazon ECS: Update your ECS service to use the new image, which will deploy the updated container.
By automating these steps with GitHub Actions, you ensure that every code change is tested and deployed seamlessly.
🔄 Rolling Updates and Blue/Green Deployments with ECS
Rolling Updates
In a rolling update, ECS replaces the old version of your application with the new one gradually. This ensures that there’s no downtime, as some instances of the old version are still running while the new version is being deployed.
Blue/Green Deployments
In a blue/green deployment, you have two environments: one for the current version (blue) and one for the new version (green). You deploy the new version to the green environment and test it. Once everything is confirmed to be working, you switch traffic from blue to green. This approach allows for zero downtime and easy rollback if needed.
📊 Infographic: CI/CD Pipeline Workflow
💡 Best Practices
- Use Secrets for Credentials: Store sensitive information like AWS credentials in GitHub Secrets.
- Monitor Deployments: Use AWS CloudWatch to monitor your ECS services and set up alarms for any issues.
- Test Before Deploying: Incorporate automated tests in your CI/CD pipeline to catch bugs early.
- Use Version Tags: Tag your Docker images with version numbers for easier tracking and rollback.
🎯 Conclusion
Implementing a CI/CD pipeline automates your deployment process, reduces errors, and allows you to deliver updates faster. By integrating GitHub Actions with Docker, ECR, and ECS, you can build a robust and efficient deployment workflow.
📣 Stay Connected!
For more tech tips and tutorials:
- 📺 Subscribe to our YouTube channel: Web Codder
- 📸 Follow us on Instagram: @web_codder_official
- 💬 Join our WhatsApp community: webcodder.dev/whatsapp
Happy coding! 💻✨