Hey there! 👋 I’m Vikas Sankhla from Web Codder. Today, I’ll guide you through something amazing called AWS ECS (Elastic Container Service). It’s a powerful way to run Docker containers in the cloud without headaches. 🤯
Let’s make it simple — like I’m explaining it to my younger cousin. 😉
🧠 What is AWS ECS?
Imagine you have a working Docker app on your laptop. Great! But what if thousands of users want to use it online? 🧍♂️🧍♀️🧍♂️
That’s where AWS ECS comes in.
🔍 In Simple Words:
ECS lets you run and manage containers in the cloud, so your app is always on, fast, and can handle traffic like a champ. 💪
📦 Why Use ECS?
- ☁️ Run Docker apps on the cloud
- ⚖️ Scale up/down automatically
- 🔒 Secure and managed by AWS
- 💸 Pay only for what you use
🏗️ Setting Up ECS: Step-by-Step
Let’s deploy a Docker container using ECS with EC2 (virtual machines).
🧩 Don’t worry — we’ll use building blocks like ECS Clusters, Tasks, and Services.
1️⃣ Step 1: Create an ECS Cluster
A Cluster is like a team of servers (EC2 instances) that will run your containers.
- Go to AWS Console > ECS
- Click “Create Cluster”
- Choose EC2 Linux + Networking
- Name it
my-cluster
2️⃣ Step 2: Register a Task Definition
A Task Definition is like a recipe 🍰. It tells ECS what to run and how.
📝 Sample Task Definition JSON:
{
"family": "my-web-task",
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "web",
"image": "nginx",
"memory": 512,
"cpu": 256,
"essential": true,
"portMappings": [
{
"containerPort": 80,
"hostPort": 80
}
]
}
]
}
📌 You can create this via Console UI or upload JSON.
3️⃣ Step 3: Launch a Service
A Service runs and maintains your tasks.
- Go to ECS > Your Cluster
- Click “Create Service”
- Choose launch type: EC2
- Select your Task Definition
- Set number of tasks (e.g., 2 for high availability)
🚀 ECS will now start your containers!
⚖️ Distributing Traffic with ALB (Application Load Balancer)
If 1000 users hit your app, you don’t want 1 server to do all the work. 😓 That’s why we use a Load Balancer.
🧩 What is ALB?
ALB is like a traffic cop 🚦. It routes incoming traffic to the right ECS container.
🛠 Setup Overview:
- Go to EC2 > Load Balancers
- Create Application Load Balancer
- Add listeners (e.g., HTTP:80)
- Register target group for ECS tasks
- Link ALB in ECS Service settings
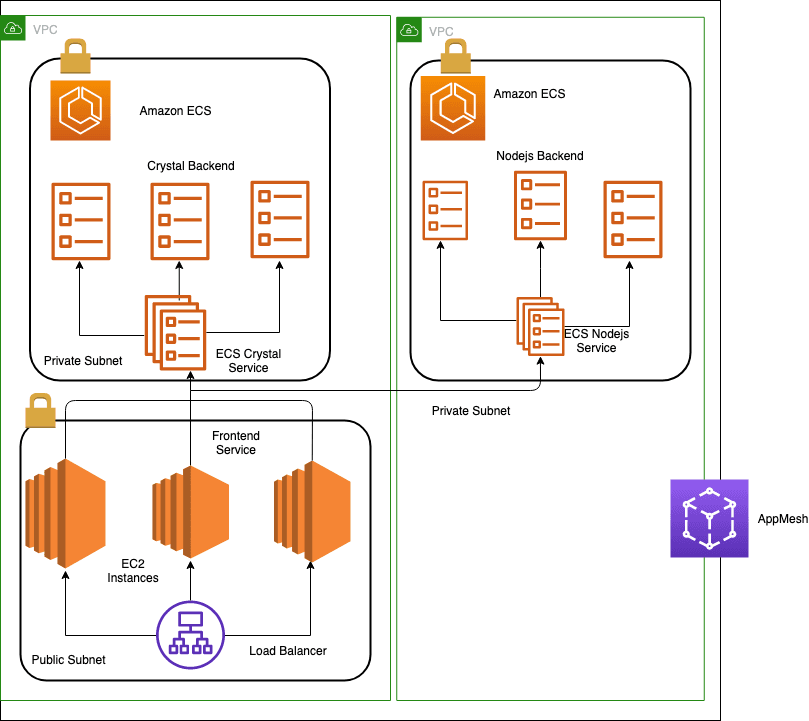
Now your app is live, scalable, and traffic-proof! 🧠✨
🧱 Key Concepts Table
| Term | What It Means |
|---|---|
| ECS | Elastic Container Service (runs Docker apps) |
| Task Definition | A recipe for your container |
| Task | One running container |
| Service | Keeps your tasks running |
| Cluster | Group of EC2 instances |
| ALB | Shares traffic across containers |
🤔 Bonus: Fargate vs EC2
| Feature | EC2 | Fargate |
|---|---|---|
| Runs On | Your EC2 instances | AWS-managed serverless |
| Setup | More control | Easier setup |
| Cost | Pay for EC2 uptime | Pay per task |
If you don’t want to manage servers, try Fargate next time. 😄
📚 Recap
Let’s go over what you’ve learned:
- ECS helps you run Docker containers in the cloud ☁️
- Task Definitions describe what to run ⚙️
- ECS Services ensure your app keeps running 🔁
- ALB shares traffic across containers ⚖️
- Fargate is a simpler, serverless alternative 🧪
📢 Final Words
That’s it, champ! Now you can launch and scale Docker apps using AWS ECS like a pro. 🧑🚀
🔔 Subscribe to learn more about cloud, devops, and full stack fun:
📺 YouTube: @web_codder
📸 Instagram: @web_codder_official
💬 Chat with us: Join WhatsApp
See you in the next guide! 💙



