Hey there, junior coder! 👋
Welcome back to your React journey with Web Codder!
Today, we’re going to unlock one of the most powerful concepts in React:
State – it’s how components remember things. 🧠💾
Let’s break it down, step by step. You’ll love this one!
📦 What is State in React?
Imagine a video game character with a health bar. 🎮
As the character takes hits or gets power-ups, the health changes.
In React, that “health” is state – data that can change over time.
🧠 In simple words:
State is a built-in React feature that lets your components:
- Remember stuff
- React to changes
- Update the UI automatically when data changes
🔄 Why Is State Important?
Without state, your web page would never change — like a printed book. 🧾
With state, your UI becomes alive!
- A like button? ➡️ State.
- A to-do list? ➡️ State.
- A dropdown menu? ➡️ State.
React uses state to decide what to show and when to re-render.
🛠 useState – The Tool That Does It All
To add state to functional components, React gives us a special tool called useState.
It’s a React Hook.
🧪 Hooks are just functions that let you “hook into” React features.
✅ How to Use useState
Let’s say you want a counter that goes up when you click a button.
Here’s how easy it is:
jsxCopyEditimport React, { useState } from "react";
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<h2>Count: {count}</h2>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increase ➕</button>
</div>
);
}
🔍 Let’s Break It Down:
| Code | What It Does |
|---|---|
useState(0) | Starts the state with 0 |
count | The current value |
setCount | A function to change the value |
setCount(count + 1) | Increases the value by 1 |
✅ When the button is clicked, the UI updates automatically!
That’s the magic of re-rendering.
📊 Visual: How useState Works
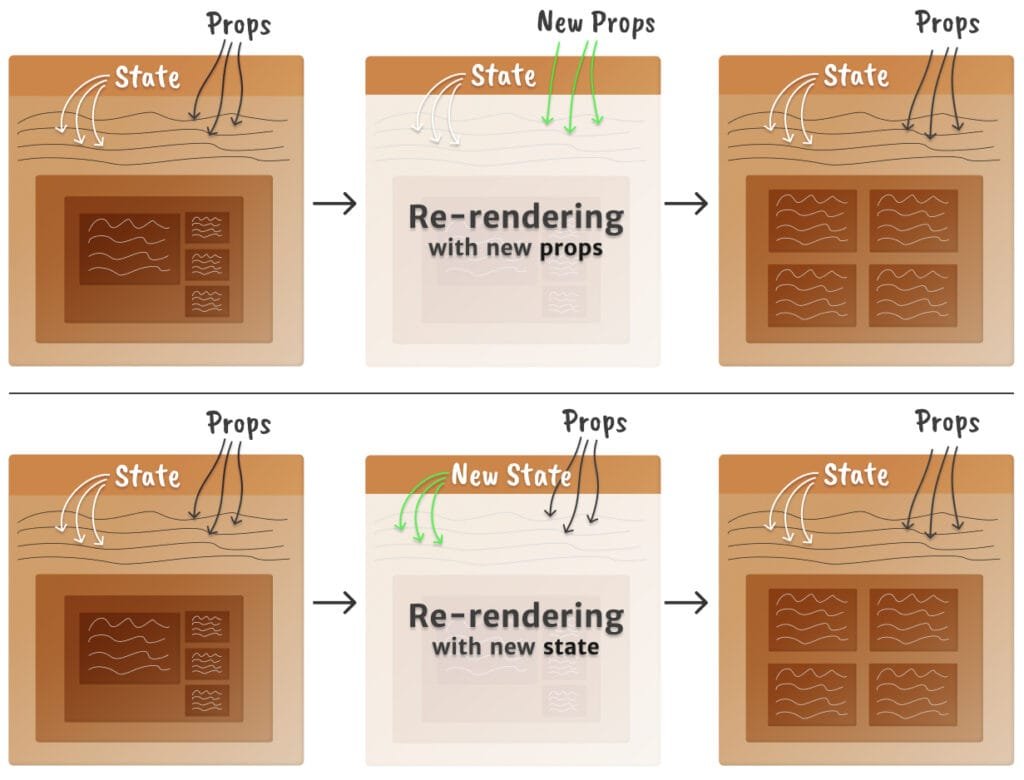
1️⃣ Initial render → 2️⃣ User clicks → 3️⃣ State updates → 4️⃣ UI refreshes
🧗 Lifting State Up – When Components Need to Share
Sometimes, two components need to talk to each other.
Imagine you have a parent component and two child components.
Both children need the same info (like a selected theme or user name).
To solve this, we lift the state up to their parent.
🧬 Example: Sharing State
jsxCopyEditfunction Parent() {
const [message, setMessage] = useState("Hi from Parent 👋");
return (
<>
<ChildA message={message} />
<ChildB onChangeMessage={setMessage} />
</>
);
}
function ChildA({ message }) {
return <p>Child A says: {message}</p>;
}
function ChildB({ onChangeMessage }) {
return (
<button onClick={() => onChangeMessage("Updated from Child B!")}>
Change Message 📝
</button>
);
}
🎉 What’s Happening?
messagelives in the ParentChildAreads itChildBupdates it- Everyone stays in sync 🧩
🧯 Conditional Rendering
Let’s say you want to show something only when a condition is true.
React makes this easy with conditional rendering.
🧪 Example: Show or Hide Content
jsxCopyEditfunction ShowHide() {
const [visible, setVisible] = useState(true);
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => setVisible(!visible)}>
{visible ? "Hide" : "Show"} Text 👁️
</button>
{visible && <p>You can see me now! 👋</p>}
</div>
);
}
visible && <p>means: only show this ifvisibleis true.
🧠 Quick Recap Table
| Concept | What It Means |
|---|---|
| State | Data that can change in a component |
| useState | A hook to add state to functional components |
| Re-rendering | UI updates when state changes |
| Lifting State Up | Moving state to a common parent to share it |
| Conditional Rendering | Show/hide things based on state |
🧠 Infographic: State in Action

App Flow: User Click → setState() → React updates → UI changes
✅ What You Can Do With State
- Build dynamic forms 📝
- Create light/dark themes 🌗
- Handle search bars 🔍
- Control toggles, modals, sliders 🎛️
State makes your React app feel alive and interactive.
🙌 Stay in the Loop – Join the Web Codder Family!
Learning React has never been this easy, right? 😊
👉 For more such content, subscribe and follow:
- 📺 YouTube: Web Codder
- 📸 Instagram: @web_codder_official
- 💬 WhatsApp: Join our community
Let’s grow together as tech buddies! 💻✨
👋 Final Thoughts
React’s state management gives your app memory, emotion, and action.
Now that you know how state works, you’re ready to build dynamic, real-world apps!
See you in the next one, coder champ! 🚀